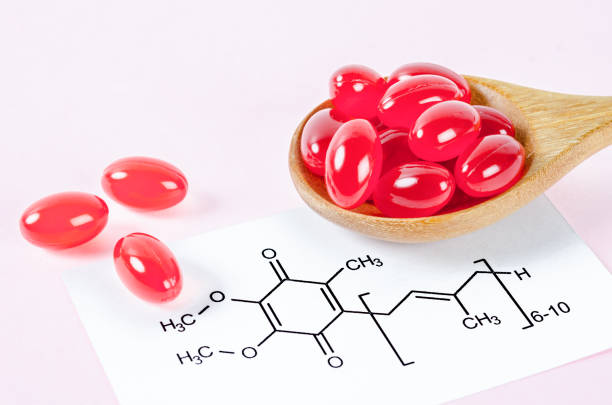
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a crucial, yet often overlooked, component of human health and well-being. Found in every cell of the body, CoQ10 plays an essential role in energy production and acts as a potent antioxidant. This article delves into the science behind CoQ10, its benefits, potential drawbacks, and its relevance in modern health practices.
What is Coenzyme Q10?
Coenzyme Q10, also known as ubiquinone, is a naturally occurring compound present in the mitochondria, the energy powerhouses of our cells. Its primary function is to aid in the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the molecule that provides energy for various cellular processes. CoQ10 is present in every cell but is found in especially high concentrations in organs with high energy demands, such as the heart, liver, and kidneys.
How CoQ10 Works
CoQ10 exists in two forms: ubiquinone (oxidized) and ubiquinol (reduced). The body converts ubiquinone to ubiquinol, which is the more active antioxidant form. This conversion is crucial because ubiquinol helps to neutralize free radicals—unstable molecules that can cause oxidative stress and damage cells.
In the mitochondria, CoQ10 facilitates the electron transport chain, a series of reactions that generate ATP. This process is fundamental to cellular respiration, providing the energy needed for muscle contraction, nerve transmission, and numerous other biological functions.
Health Benefits of CoQ10
- Energy Production: One of the most well-known benefits of CoQ10 is its role in boosting energy levels. By enhancing ATP production, CoQ10 helps improve overall vitality and stamina, which can be particularly beneficial for individuals with chronic fatigue or those undergoing intense physical activity.
- Cardiovascular Health: CoQ10 is critical for heart health. It supports the function of the heart muscle and helps maintain healthy blood vessels. Some studies suggest that CoQ10 supplementation can help reduce symptoms of congestive heart failure, lower blood pressure, and improve overall cardiovascular function.
- Antioxidant Protection: As an antioxidant, CoQ10 helps protect cells from oxidative damage caused by free radicals. This protective role is essential for reducing inflammation and supporting overall cellular health.
- Brain Health: The brain, with its high metabolic activity, benefits from CoQ10’s energy-boosting properties. Research indicates that CoQ10 may support cognitive function and protect against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s by mitigating oxidative stress and improving mitochondrial function.
- Skin Health: CoQ10 is also beneficial for the skin. It can enhance skin elasticity, reduce wrinkles, and promote overall skin health by neutralizing oxidative damage and supporting cellular repair processes.
CoQ10 Deficiency and Supplementation
Deficiency Causes: CoQ10 levels naturally decline with age, and certain health conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, and neurodegenerative disorders, can also lead to lower CoQ10 levels. Additionally, some medications, notably statins used to lower cholesterol, can reduce CoQ10 levels as they inhibit its synthesis.
Supplementation: CoQ10 supplements are available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and soft gels. The most common forms are ubiquinone and ubiquinol. While both forms are effective, ubiquinol is generally considered to be more bioavailable, meaning it is more easily absorbed by the body.
Dosage: Typical dosages range from 100 to 300 milligrams per day, though specific needs can vary based on individual health conditions and goals. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen, particularly if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.
Potential Side Effects and Interactions
CoQ10 is generally well-tolerated, with most people experiencing minimal side effects. However, some individuals may experience mild gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, diarrhea, or abdominal discomfort. Rarely, allergic reactions or headaches may occur.
CoQ10 supplements can interact with certain medications. For instance, they may reduce the effectiveness of blood-thinning medications like warfarin. Additionally, because CoQ10 plays a role in lowering blood pressure, it may enhance the effects of antihypertensive drugs. It is crucial to discuss potential interactions with a healthcare provider, especially if you are on medication or have a chronic health condition.
The Future of CoQ10 Research
Ongoing research continues to explore the full range of CoQ10’s benefits and its potential therapeutic uses. Studies are investigating its role in conditions such as cancer, diabetes, and migraines. Additionally, researchers are examining how CoQ10 supplementation can be integrated into preventive healthcare strategies to support aging populations and improve quality of life.
Conclusion
Coenzyme Q10 is a vital component of our cellular machinery, with far-reaching implications for overall health and well-being. Its role in energy production, cardiovascular health, antioxidant protection, and more makes it a valuable nutrient for maintaining optimal health. While CoQ10 deficiency can impact various aspects of health, supplementation offers a promising way to support bodily functions and address specific health concerns.
As with any supplement, it is essential to approach CoQ10 with an informed perspective. Consulting with healthcare professionals and staying updated on the latest research can help individuals make informed decisions about incorporating CoQ10 into their health regimen. Whether you’re seeking to boost your energy levels, support heart health, or enhance cognitive function, CoQ10 remains a noteworthy ally in the pursuit of better health.